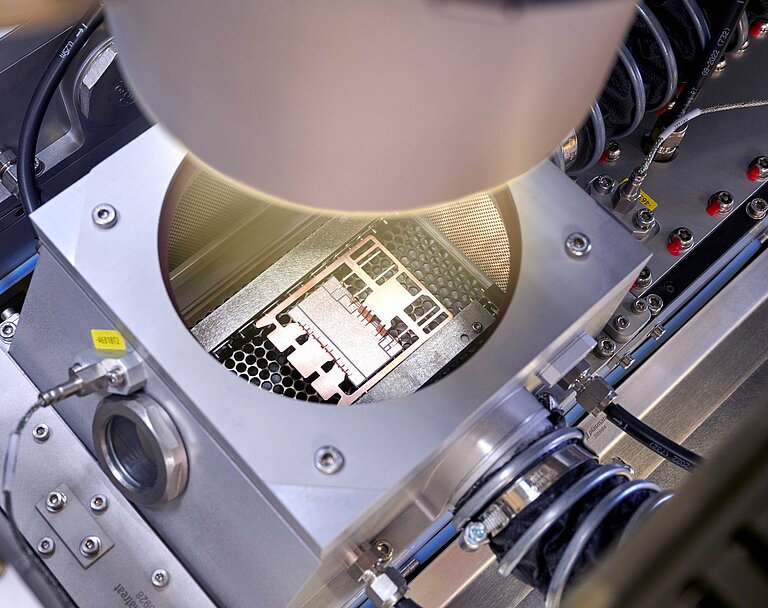
Plasma Technology in Action – Live at PCIM Europe 2025
Power modules are the core of modern power electronics – whether in e-mobility, industrial automation, or renewable energy applications. From May 6–8, 2025, Plasmatreat will be showcasing how plasma technology can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of these critical components at PCIM Europe in Nuremberg.
At booth 169 in Hall 7, we’ll demonstrate live how oxide layers can be removed automatically and inline, and how our PlasmaPlus® coating technology effectively prevents delamination during overmolding. Visit us on-site and discover what future-ready surface treatment looks like – precise, cleanroom-compatible, and environmentally friendly.
Challenges in Semiconductor and Power Module Production

Tough Demands on Materials and Interconnections
High-performance power modules must operate reliably for years under extreme conditions. Whether in electric vehicles, wind turbines, or industrial drives, these components are exposed to high temperatures, high voltages, and intense mechanical stress – all within increasingly compact designs.
A particular challenge lies at so-called “triple points,” where different materials such as copper, ceramics, and potting compounds meet. These zones are prone to stress, trapped air, or adhesion failure – all of which can shorten the module’s lifespan. One of the root causes: oxidized metal surfaces that compromise solderability and increase contact resistance. Epoxy delamination during overmolding is another common risk. To address these issues, reliable interconnect technology and targeted surface treatment are essential.
Live Demo at PCIM Europe
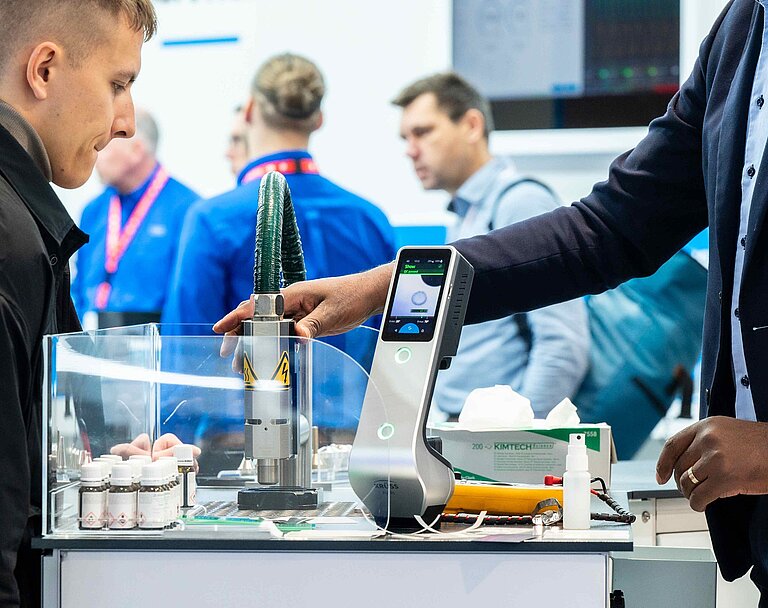
Experience our plasma technology live at booth 169 in Hall 7. In a fully automated demo cell, we’ll showcase both REDOX-based inline oxide reduction and functional nanocoating with PlasmaPlus® – all under realistic production conditions.
A highlight of our exhibit is the robot-controlled Plasma Treatment Unit (PTU), which allows for accurate, non-contact treatment of even complex geometries. At our interactive plasma demonstration table, you can see and feel the effects of plasma treatment for yourself – from surface cleaning and activation to improved wettability.
Our on-site experts are available to advise you on how our technologies can be tailored to your specific applications and processes.

Use Cases – Where Plasma Makes the Difference
Application Areas Across High-Demand Industries
Our plasma systems are used wherever power modules are exposed to extreme conditions and need to perform reliably. Different industries face different challenges – but the solution remains the same: advanced surface treatment with Openair-Plasma® and PlasmaPlus®.
E-Mobility
In inverters, battery management systems, and charging units, plasma ensures stable electrical contacts and prevents delamination in highly dynamic environments with intense heat and current loads.
Renewable Energy
Photovoltaic and wind energy systems require long-term durability despite exposure to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature swings. Plasma coatings help protect critical contact areas and improve reliability.
Industrial Automation
Power modules in industrial and robotic systems must withstand vibration, dust, and harsh media. Plasma treatment improves adhesion of potting compounds and ensures long-lasting, high-integrity connections.
The Exhibition Warm-Up: Power Module PlasmaTalk Now Online
Entre los principales retos figuran:
Huecos en uniones soldadas
- Impedancia térmica y eléctrica: Los huecos pueden reducir la conductividad térmica y eléctrica de las juntas de soldadura. Esto puede provocar puntos calientes, aumento de la resistencia y posibles fallos por sobrecalentamiento.
- Debilidad mecánica: Los huecos comprometen la integridad mecánica de las uniones soldadas, haciéndolas más susceptibles de agrietarse y fallar bajo estrés térmico y mecánico.
Oxidación de las superficies metálicas
- Adhesión deficiente: Las superficies oxidadas dificultan la correcta unión entre los materiales, lo que puede provocar delaminación o una resistencia mecánica deficiente de los componentes ensamblados.
- Soldadura inconsistente: Los óxidos crean barreras que impiden que la soldadura se humedezca y se extienda uniformemente, lo que da lugar a uniones soldadas débiles y poco fiables.
Compatibilidad de materiales
- Desajuste de la expansión térmica: Los distintos materiales tienen diferentes coeficientes de dilatación térmica. Sin un tratamiento adecuado de la superficie y técnicas de unión, los ciclos térmicos pueden causar tensiones que conducen a la delaminación o agrietamiento.
- Incompatibilidad química: Los materiales deben seleccionarse y tratarse cuidadosamente para evitar reacciones químicas que puedan degradar el rendimiento o provocar fallos.
Residuo de fundente
- Contaminación: Los residuos de fundente pueden contaminar el conjunto, provocando cortocircuitos eléctricos, corrosión y problemas de fiabilidad.
- Desafíos de limpieza: A medida que los componentes se hacen más pequeños y están más densamente empaquetados, la eliminar los residuos de fundente sin dañar los componentes se hace cada vez más difícil.
Miniaturización
- Requisitos de precisión: Los componentes más pequeños y los pasos más finos requieren procesos de fabricación extremadamente precisos. Incluso las más pequeñas imperfecciones pueden provocar problemas de rendimiento o fallos importantes.
- Disipación del calor: La disipación eficiente del calor se vuelve más desafiante a medida que disminuye el tamaño de los componentes, lo que requiere de materiales y juntas de soldadura de alta calidad para gestionar el calor de forma eficaz.
Fiabilidad a largo plazo
- Exposición ambiental: La electrónica de potencia suele estar expuesta a entornos adversos, como altas temperaturas, humedad y vibraciones. Garantizar que todos los materiales y juntas estén libres de huecos y defectos es fundamental para mantener la fiabilidad a largo plazo.
- Envejecimiento y degradación: Con el tiempo, los materiales se degradan y las juntas se debilitan. Los huecos y las imperfecciones aceleran este proceso, provocando fallos prematuros.

Cómo afrontar estos desafíos
Técnicas como la tecnología Openair-Plasma® y la reducción de óxido en línea con REDOX-Tool pueden limpiar y preparar eficazmente las superficies, garantizando que todos los materiales se adhieran correctamente y funcionen de forma fiable incluso bajo las altas exigencias de la electrónica de potencia.
El resultado es un mejor rendimiento eléctrico, mayores índices de producción, una mayor fiabilidad y longevidad de los componentes.